System Design: What is Availability?
#22 - Availability
In this blog, we'll explore the concept of availability, availability tiers, strategies to improve availability, and best practices for achieving high availability.
What is Availability?
Availability refers to the proportion of time a system is operational and accessible when required.
It is usually expressed as a percentage, indicating the system's uptime over a specific period.
The formal definition of availability is:
Availability = Uptime / (Uptime + Downtime)Uptime: The period during which a system is functional and accessible.
Downtime: The period during which a system is unavailable due to failures, maintenance, or other issues.
If you’re enjoying this newsletter and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you'll unlock all premium articles and gain full access to all premium courses on algomaster.io.
Availability Tiers
Availability is often expressed in "nines". The higher the availability, the less downtime there is.
Each additional "nine" represents an order of magnitude improvement in availability.
Example: 99.99% availability represents a 10-fold improvement in uptime compared to 99.9%.
Strategies for Improving Availability
1. Redundancy
Redundancy involves having backup components that can take over when primary components fail.
Techniques:
Server Redundancy: Deploying multiple servers to handle requests, ensuring that if one server fails, others can continue to provide service.
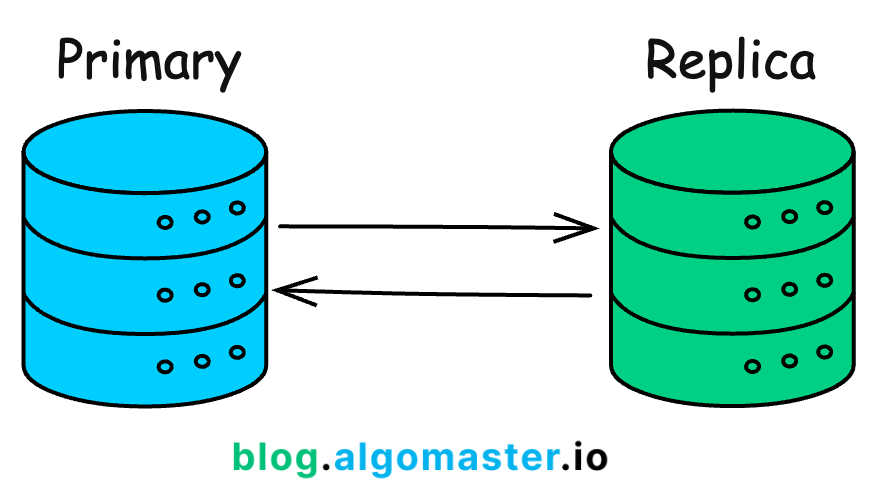
Database Redundancy: Creating a replica database that can take over if the primary database fails.
Geographic Redundancy: Distributing resources across multiple geographic locations to mitigate the impact of regional failures.
2. Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes a bottleneck, enhancing both performance and availability.
Techniques:
Hardware Load Balancers: Physical devices that distribute traffic based on pre-configured rules.
Software Load Balancers: Software solutions that manage traffic distribution, such as HAProxy, Nginx, or cloud-based solutions like AWS Elastic Load Balancer.
3. Failover Mechanisms
Failover mechanisms automatically switch to a redundant system when a failure is detected.
Techniques:
Active-Passive Failover: A primary active component is backed by a passive standby component that takes over upon failure.
Active-Active Failover: All components are active and share the load. If one fails, the remaining components continue to handle the load seamlessly.
4. Data Replication
Data replication involves copying data from one location to another to ensure that data is available even if one location fails.
Techniques:
Synchronous Replication: Data is replicated in real-time to ensure consistency across locations.
Asynchronous Replication: Data is replicated with a delay, which can be more efficient but may result in slight data inconsistencies.
5. Monitoring and Alerts
Continuous health monitoring involves checking the status of system components to detect failures early and trigger alerts for immediate action.
Techniques:
Heartbeat Signals: Regular signals sent between components to check their status.
Health Checks: Automated scripts or tools that perform regular health checks on components.
Alerting Systems: Tools like PagerDuty or OpsGenie that notify administrators of detected issues.
Best Practices for High Availability
Design for Failure: Assume that any component of your system can fail at any time and design your system accordingly.
Implement Health Checks: Regular health checks allow you to detect and respond to issues before they become critical failures.
Use Multiple Availability Zones: Distribute your system across different data centers to prevent localized failures.
Practice Chaos Engineering: Intentionally introduce failures to test system resilience.
Implement Circuit Breakers: Prevent cascading failures by quickly cutting off problematic services.
Use Caching Wisely: Caching can improve availability by reducing load on backend systems.
Plan for Capacity: Ensure your system can handle both expected and unexpected load increases.
Availability is a critical aspect of system design that ensures users can access services reliably and continuously.
By implementing strategies like redundancy, load balancing, failover mechanisms, and data replication, you can design highly available systems.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re enjoying this newsletter and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you'll unlock all premium articles and gain full access to all premium courses on algomaster.io.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish








Useful
Database Redundancy and Data Replication are the same things right?